REDAffectiveLM: Leveraging Affect Enriched Embedding and Transformer-based Neural Language Model for Readers' Emotion Detection
| Anoop K.1, Deepak P.2,Manjary P. Gangan1, Savitha Sam Abraham3, Lajish V. L.1 1Department of Computer Science, University of Calicut, India 2School of Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Queen’s University Belfast, UK. 3 School of Science and Technology, Örebro University, Sweden. |  |
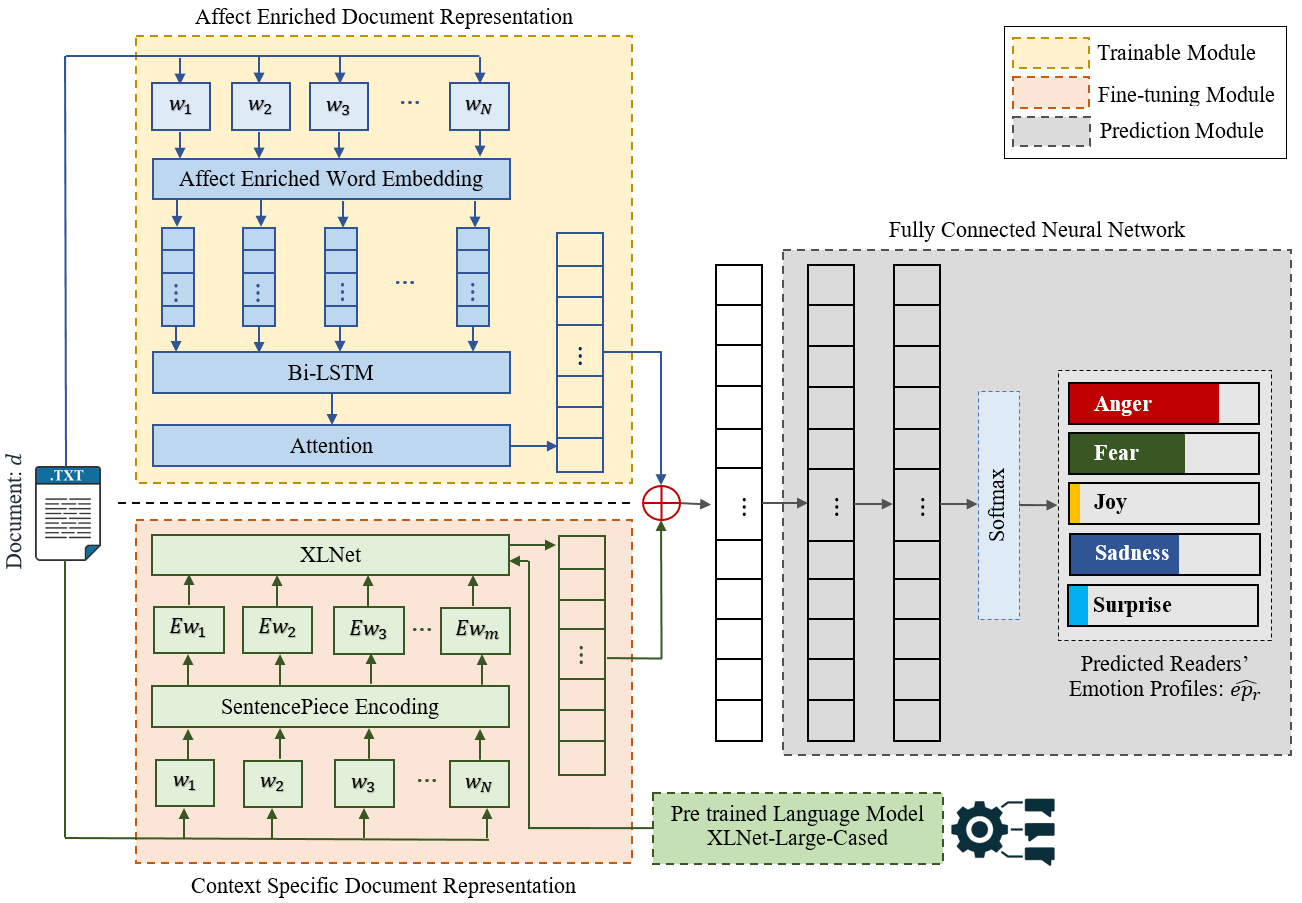
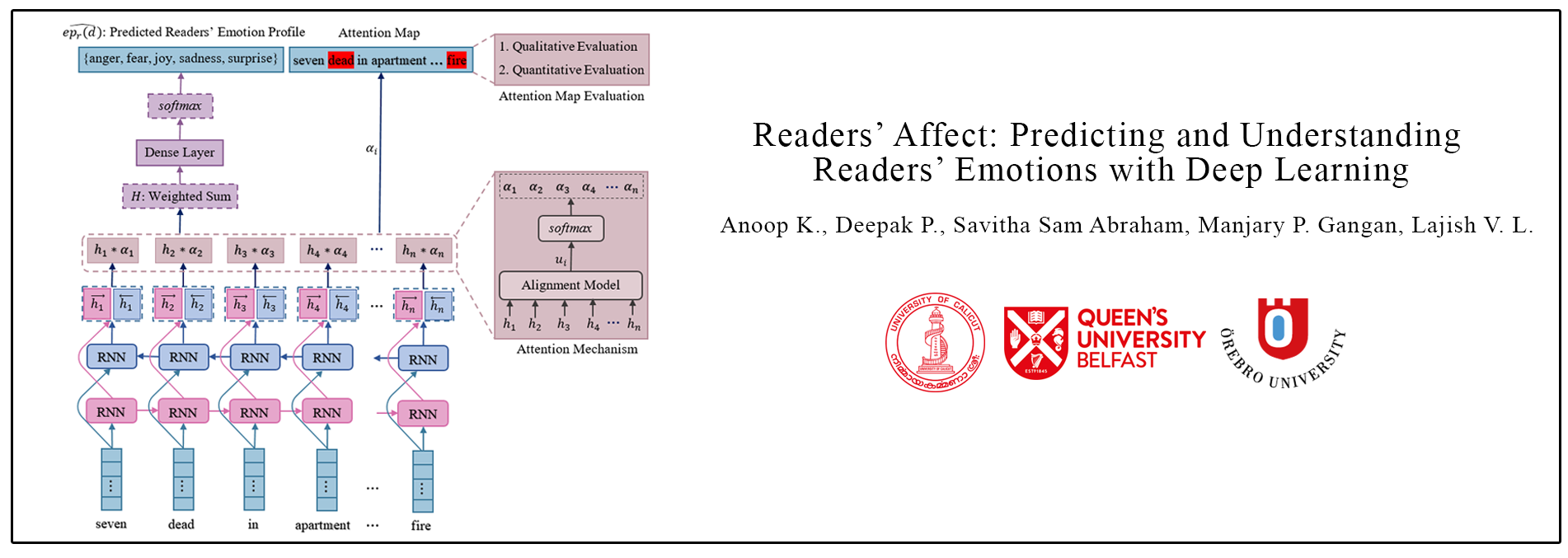
Abstract: Technological advancements in web platforms allow people to express and share emotions towards textual write-ups written and shared by others. This brings about different interesting domains for analysis; emotion expressed by the writer and emotion elicited from the readers. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for Readers' Emotion Detection from short-text documents using a deep learning model called REDAffectiveLM. Within state-of-the-art NLP tasks, it is well understood that utilizing context-specific representations from transformer-based pre-trained language models helps achieve improved performance. Within this affective computing task, we explore how incorporating affective information can further enhance performance. Towards this, we leverage context-specific and affect enriched representations by using a transformer-based pre-trained language model in tandem with affect enriched Bi-LSTM+Attention. For empirical evaluation, we procure a new dataset REN-20k, besides using RENh-4k and SemEval-2007. We evaluate the performance of our REDAffectiveLM rigorously across these datasets, against a vast set of state-of-the-art baselines, where our model consistently outperforms baselines and obtains statistically significant results. Our results establish that utilizing affect enriched representation along with context-specific representation within a neural architecture can considerably enhance readers' emotion detection. Since the impact of affect enrichment specifically in readers' emotion detection isn't well explored, we conduct a detailed analysis over affect enriched Bi-LSTM+Attention using qualitative and quantitative model behavior evaluation techniques. We observe that compared to conventional semantic embedding, affect enriched embedding increases the ability of the network to effectively identify and assign weightage to the key terms responsible for readers' emotion detection to improve prediction.
📝 Paper(pre-print): https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.08995
🌍 GitHub: https://github.com/anoopkdcs/REDAffectiveLM
🌍 Dataset: https://dcs.uoc.ac.in/cida/resources/ren-20k.html
People
- 1. Anoop K , University of Calicut, Kerala, India. (anoopk_dcs@uoc.ac.in)
- 2. Deepk P. , Queen’s University Belfast, Northern Ireland, UK. (deepaksp@acm.org)
- 3. Manjary P Gangan , University of Calicut, Kerala, India.
- 4. Savitha Sam Abraham, School of Science and Technology, Örebro University, Sweden.
- 5. Lajish V L, University of Calicut, Kerala, India.
Other Related Work