Introduction
Emotions are highly useful to model human behavior being at the core of what makes us human. Today, people abundantly express and share emotions through social media. Technological advancements in such platforms enable sharing opinions or expressing any specific emotions towards what others have shared, mainly in the form of textual data. This entails an interesting arena for analysis; as to whether there is a disconnect between the writer’s intended emotion and the reader’s perception of textual content.In this context we procure a Readers’ Emotion News datasets by using the social news network, Rappler and its award-winning Mood Meter widget. Mood Meter enables readers to cast their emotion votes towards several categories of emotions (Afraid, Amused, Angry, Annoyed, Don’t care, Happy, Inspired, and Sad) and records the total percentage of votes obtained for each emotion. Unlike other sources, we choose Rappler due to its simplicity, popularity, and ease of organizing several news articles under multiple genres and associated emotion profiles. We manually collect only the popular news articles by checking for high emotion votings represented in the Rappler Mood Meter, to ensure that the selected news articles have a high social reach. REN-20k is our newly curated Readers’ Emotion News dataset procured in a similar fashion of RENh-4k from the popular online news network Rappler, where we collect news articles manually, from the year span 2014 to 2019, by checking articles with high emotion votings in the Mood Meter widget of Rappler indicating high popularity and social reach of these articles. But it is an advanced version containing 20474 numbers of documents with corresponding readers' emotion profiles collected for diverse classes of emotions Afraid, Amused, Angry, Annoyed, Don't care, Happy, Inspired, and Sad. Also, each document consists of the whole news content including headlines, abstract and full-length news story excluding images and videos, making it a long-text dataset with average words per document as 527.84. With the help of genre information available in the portal and by manual annotations, we assign each document to a diverse set of genres, Business, Entertainment, Lifestyle, Sports, Technology and Others, unlike RENh-4k that considers only three genres, Health \& well-being, Social issues and Others.
Dataset Sample
News Headline: Countries ban China arrivals as virus death toll hits 213
News Abstract: Nearly 10,000 people have been infected in China by the new coronavirus and new cases are found abroad, with more than ...
News Content: BEIJING, China – Countries stepped up travel restrictions on arrivals from China on Friday, January 31, after a global health emergency was declared over a viral epidemic that has killed 213 people. Nearly 10,000 people have been infected in China by the new coronavirus and ...
News Category: Health & well-being
Readers' Emotion:
People
- Anoop K, University of Calicut, Kerala, India. (anoopk_dcs@uoc.ac.in)
- Deepak P, Queen’s University Belfast, Northern Ireland, UK. (deepaksp@acm.org)
- Manjary P Gangan, University of Calicut, Kerala, India.
- Savitha Sam Abraham , School of Science and Technology, Örebro University, Örebro, Sweden.
- Lajish V L, University of Calicut, Kerala, India.
Publication
Anoop Kadan, Deepak P., Manjary P. Gangan, Savitha Sam Abraham, Lajish V. L. REDAffectiveLM: Leveraging Affect Enriched Embedding and Transformer-based Neural Language Model for Readers' Emotion Detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.08995 (2023) DOI: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2301.08995
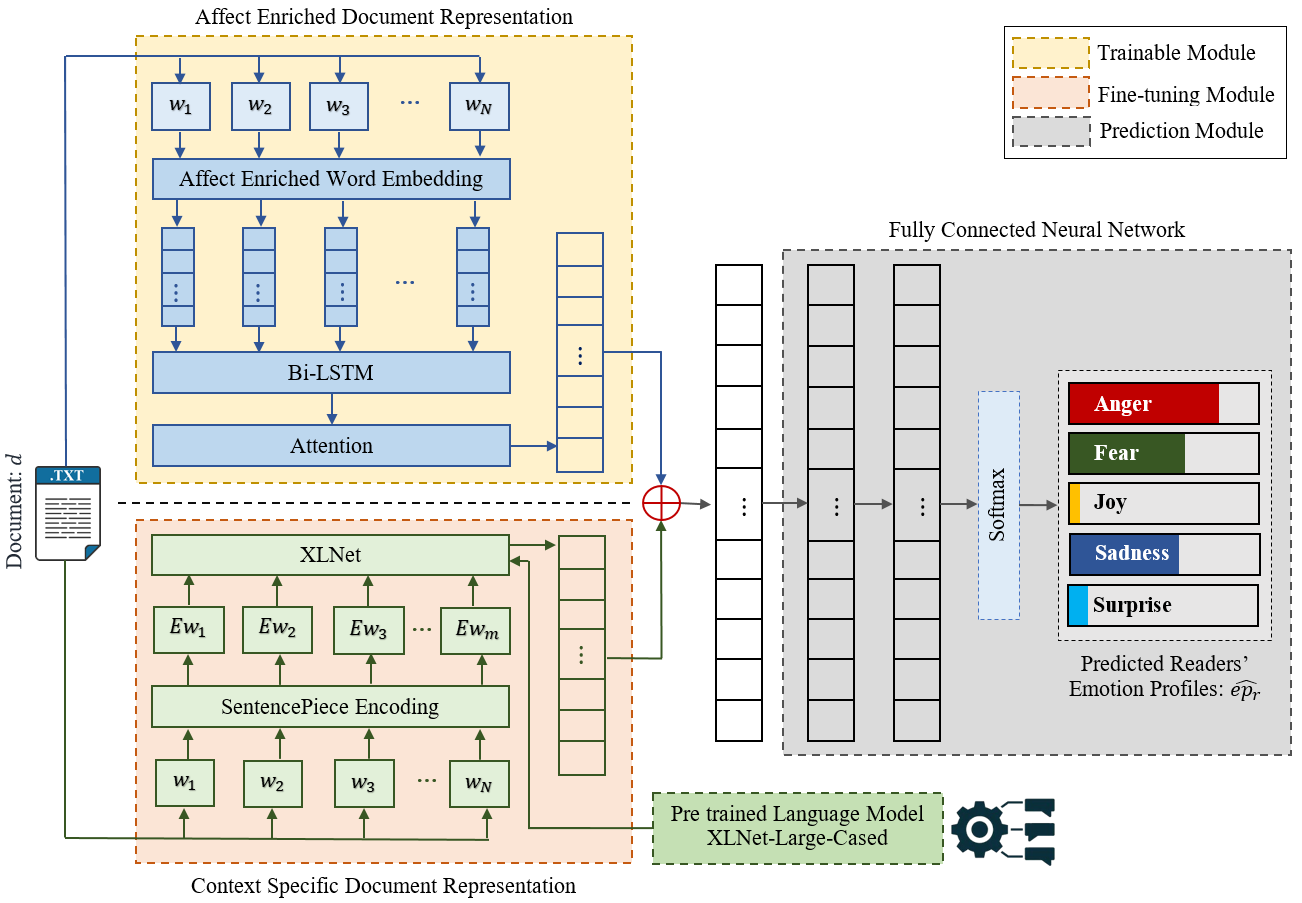
Abstract: Technological advancements in web platforms allow people to express and share emotions towards textual write-ups written and shared by others. This brings about different interesting domains for analysis; emotion expressed by the writer and emotion elicited from the readers. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for Readers' Emotion Detection from short-text documents using a deep learning model called REDAffectiveLM. Within state-of-the-art NLP tasks, it is well understood that utilizing context-specific representations from transformer-based pre-trained language models helps achieve improved performance. Within this affective computing task, we explore how incorporating affective information can further enhance performance. Towards this, we leverage context-specific and affect enriched representations by using a transformer-based pre-trained language model in tandem with affect enriched Bi-LSTM+Attention. For empirical evaluation, we procure a new dataset REN-20k, besides using RENh-4k and SemEval-2007. We evaluate the performance of our REDAffectiveLM rigorously across these datasets, against a vast set of state-of-the-art baselines, where our model consistently outperforms baselines and obtains statistically significant results. Our results establish that utilizing affect enriched representation along with context-specific representation within a neural architecture can considerably enhance readers' emotion detection. Since the impact of affect enrichment specifically in readers' emotion detection isn't well explored, we conduct a detailed analysis over affect enriched Bi-LSTM+Attention using qualitative and quantitative model behavior evaluation techniques. We observe that compared to conventional semantic embedding, affect enriched embedding increases the ability of the network to effectively identify and assign weightage to the key terms responsible for readers' emotion detection to improve prediction.